Everything You Need to Know About Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)

Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) provides a systematic approach based on rules and regulations for organisations to achieve intended outcomes. Moreover, it ensures the manufacture of safe and high-quality goods consistently across diverse industries, including the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetics sectors. In this blog, we will cover everything about GMP, from its significance to its guiding principles and methods. What is Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)? Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is a quality measuring system. Moreover, it describes the rules and guidelines necessary for organisations, from production and testing to the distribution of goods. GMP seeks to reduce production hazards by conducting a risk assessment to eliminate potential risks and testing the finished product. It is significant for products which directly impact consumers’ health and safety. Importance of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) is essential for ensuring the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products. Furthermore, it demonstrates an organisation’s dedication to guidelines for manufacturing processes and maintaining regulatory compliance. It offers a goldmine of benefits to an organisation; these are: Benefits of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) ⮯ GMP ensures the safety and quality of products by minimising the risk of contamination, adulteration, and other quality issues. Moreover, this directly safeguards consumer health and well-being. GMP ensures consistent product quality by establishing stringent standards and procedures and helps companies maintain their reputation and customer trust. Many regulatory agencies, such as the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in the United States and the EMA (European Medicines Agency) in Europe, require companies to adhere to GMP guidelines. However, Non-compliance to GMP regulations can lead to legal and financial consequences. Implementing Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) can reduce the likelihood of costly product recalls, fines, and legal disputes, ultimately saving companies money. Principles of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) ⮯ The Eight principles of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are as follows :- Documentation – It provides a comprehensive and accurate documentation approach for various business processes and procedures. Moreover, this includes batch records, standard operating procedures (SOPs), and quality control documents. Personnel – GMP guidelines mandate organisations to provide employees with proper training and hygiene practices to prevent contamination and ensure product quality. Facilities and Equipment – It states that adequate facilities and well-maintained equipment are necessary to maintain a clean and controlled manufacturing environment. Process Control – GMP focuses on consistency in manufacturing processes through strict process control measures, ensuring each batch meets quality standards. Raw Materials – The quality and source of raw materials are closely monitored and controlled to prevent contamination or adulteration. Packaging and Labelling – It follows appropriate packaging and labelling practices to manage mix-ups by ensuring accurate product information. Quality Control and Testing – GMP follows rigorous quality control and testing procedures at various stages of production to verify product quality. Records and Traceability – GMP mandates organisations to maintain detailed records of each batch to enable traceability. Which industries can apply for Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) Certification? A list of industries that can apply for GMP Certification: Pharmaceuticals Food and Beverage Cosmetics Medical Device Herbal and Dietary Supplements Implementation of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) Certification Organisations can follow these steps to implement Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) Certification. These are: An organisation must assign a team responsible for GMP compliance and training. Organisations must create and document GMP procedures tailored to their specific industry and product needs and requirements. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) provide thorough training to employees on GMP principles, hygiene, and procedures. It mandates organisations to conduct regular internal audits and inspections to identify and rectify compliance issues. Continuous Improvement is an integral principle that monitors and improves GMP practices based on feedback and evolving industry standards. Conclusion ✅ Companies can obtain Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to win consumers trust and confidence. Moreover, it demonstrates an organisation’s commitment to safety and product quality by meeting quality regulations and GMP principles. Understanding and using GMP is essential for success and public trust, regardless of whether you are in the pharmaceutical, food, cosmetic, or any other business. Enjoy Reading – Guide For Food Safety Certifications
Beware of Fake Claims: Websites Claiming to be a Certification Partner with SIS Certifications
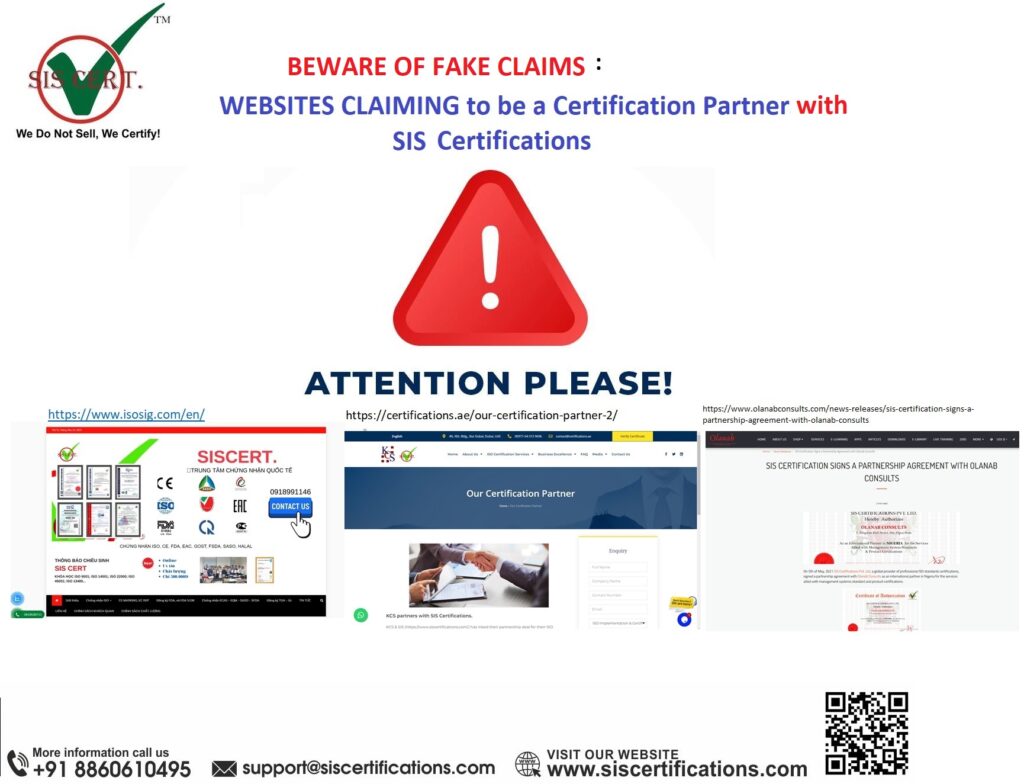
SIS Certifications would like to enlighten and make the public aware that there are certain websites falsely claiming to be a certification partners of SIS Certifications Pvt. Ltd. These websites are not affiliated with SIS Certification and are not authorized to issue ISO certifications. SIS Certifications wants to inform you that these websites are not legitimate and that any ISO certification issued by them would not be recognized by SIS Certification or any other accredited ISO certification body. In today’s digital age, it is unfortunate that some websites are falsely claiming to be certification partners of SIS Certifications. As a responsible individual, it is crucial to take the necessary steps to protect yourself and others from falling into their influence. First and foremost, it is important to verify the authenticity of any website or organization claiming to be a certification partner of SIS Certifications. Visit the official website of SIS Certifications and cross-reference the list of certified partners provided by them. This will help you identify legitimate partners and avoid fraudulent ones. Additionally, be cautious of any websites that offer certifications at unusually low prices or promise quick and easy certification processes. Legitimate certification programs often require time, effort, and thorough evaluation before granting certifications. If you come across a website that falsely claims to be a certification partner of SIS Certifications, report it immediately. Contact SIS Certifications directly through their official channels and provide them with all relevant information regarding the fraudulent website. This will help them take appropriate action against such deceptive practices. Lastly, spread awareness among your peers and colleagues about these false claims. Share this information on social media platforms or within professional networks to ensure that others are also aware of the potential risks associated with these deceptive websites. while taking these necessary steps, you can collectively safeguard yourself and others from falling victim to false claims made by unauthorized websites posing as certification partners of SIS Certifications. Stay vigilant and prioritize authenticity when seeking certifications or partnerships to maintain credibility in your professional endeavours. SIS Certifications Pvt Ltd is a wholly owned ISO Certification Body and does not have any PARTNERSHIP with these websites. Please do not trust THESE FOLLOWING WEBSITES AND REFRAIN FROM DOING BUSINESS WITH THEM ON BEHALF OF SIS CERTIFICATIONS. https://www.olanabconsults.com https://certifications.ae https://www.isosig.com/en/ olanabconsults.comWe would like to clarify a matter concerning a former associate, Olanab Consulting Ltd, which was previously engaged with SIS Certifications under an associate partnership agreement in 2021. Following the issuance of certifications to their referred clients, our Accreditation Board raised serious concerns regarding the nature of Olanab Consulting Ltd as a consultancy organization. As per the compliance requirements under ISO/IEC 17021-1, and to maintain the integrity, impartiality, and transparency of the certification process, the associate agreement with Olanab Consulting Ltd was immediately terminated. The organization was officially instructed to remove all claims or references indicating an active association with SIS Certifications. However, despite clear instructions and formal communication, Olanab Consulting Ltd has continued to promote misleading content on its website, including reposting outdated and invalid email communication from our marketing team. These emails were exchanged at the time when the agreement was still valid and hold no relevance or validity after the termination. Furthermore, we have documented evidence where the unauthorized use of our brand name was acknowledged by Olanab, along with their admission that such representation was intended for mutual benefit-a clear violation of the compliance and ethical boundaries between a certification body and a consultant. We urge all stakeholders, clients, and interested parties to verify any claims of partnership or association with SIS Certifications only through our official communication channels or verified website links. We remain committed to upholding the highest standards of transparency, impartiality, and integrity in our operations. Certifications.aeCertifications.ae is a consultancy firm. According to the guidelines set by ISO/IEC 17021, SIS Certifications, being a certification body, is not permitted to have any business relationship with consultants. As per the latest information dated 19/06/2025 Certifications.ae has removed all content and references associated with SIS Certifications from its platforms. The issue has been mutually addressed and resolved by both parties. Isosig.comIsosig.com is a free parked page and was found to be entirely fake. As per the latest information dated June 19, 2025, Isosig.com has removed all content and references related to SIS Certifications from its platform. The matter has been resolved. SIS Certifications is one of the most trusted certification bodies. Our journey started in 2013 and since then we have grown to cater to clients in several countries .We are accredited by International Accreditation Services (IAS-IAF) .Our highly qualified team of experts offer their services in auditing management systems against the requirements of respective ISO certifications. If you would like more information about this topic please contact Mr Arunendra Dvivedi 📞 +91 8860610495📧 [email protected]
The Importance of ISO 13485 Certification in The Medical Device Industry

Are you ready to step into the world of medical device manufacturing? Hold on tight as we explore ISO 13485 certification, a crucial component of the jigsaw. This certification guarantees that producers follow stringent quality management systems in a sector where accuracy and safety are crucial requirements. Join us as we explore the significance of ISO 13485 and learn how it plays a crucial part in saving lives every day, whether you are already familiar with it or are just beginning your path in the medical device sector. So buckle up, and let’s go on this enlightening journey together! Introduction: Understanding ISO 13485 and its Significance ISO 14001 standard for the Environmental It is impossible to overstate the significance of ISO certification for the medical device sector. You must uphold stringent quality standards if you want to guarantee that your gadgets are reliable and secure. The ISO 13485 standard is among the most significant ones for medical equipment. The worldwide ISO 13485 standard was created exclusively for medical equipment. It lays up the specifications for a thorough quality management system, including design and development, manufacturing, storage and distribution, customer support, and post-market monitoring. There are numerous advantages to implementing an ISO 13485-based quality management system. Most significantly, it aids in making sure that your devices comply with all relevant regulatory requirements. Additionally, it can aid in enhancing cooperation and communication within your business as well as with clients and suppliers. You can save costs related to rework or scrap by using ISO 13485 while simultaneously increasing product quality and consistency. Although ISO 13485 accreditation has several advantages, probably the most significant one is that it promotes patient safety. You commit to creating safe and reliable medical devices when you establish a quality management system based on this standard. The fact that it offers producers a competitive edge in the market is arguably the most significant advantage. ISO 13485:2016 medical devices demonstrate to potential customers that a manufacturer is committed to quality and safety. It aids in improving a manufacturer’s internal processes and procedures. The ISO 13485 certification may aid medical device manufacturers in streamlining their processes, providing better customer service, and growing their clientele. Management Systems (EMS) offers a framework that businesses may use to enhance their environmental performance. The objective of the EMS is to reduce the adverse effects of business operations, products, and services while maintaining compliance with relevant environmental laws. It promotes a process-based approach to maintaining environmental management by highlighting the necessity of establishing goals, tracking results, and making data-driven decisions. ISO 13485 Certification Requirement ⮯ Although implementing ISO 13485 may seem difficult or intimidating, in practice, doing so helps get rid of some of the regulations and methods that are random in the medical device industry. A quality management system (QMS) must be designed and kept up to date, and it must contain documentation, internal audits, and remedial measures. Risk management system: To detect and assess any possible hazards associated with the medical device throughout the duration of its lifespan, teams must also establish a risk management plan. Verification of compliance: According to ISO 13485, businesses must ensure that their products meet both customer and legal requirements. This involves upholding traceability and record-keeping mechanisms to ensure that items are recognised and tracked along the supply chain. Organisations should set up and maintain a system for the control of non-conforming items to make sure that any issues are identified and dealt with as soon as possible. The medical device sector could start to experience some harmonisation and uniformity of systems and procedures as ISO 13485 is increasingly adopted globally by businesses and governmental organisations. The industry will become more organised as a result of this standardisation, and significant inventions will have an easier and maybe quicker path to market. Maintaining ISO 13485 Compliance: Best Practices for Ongoing Success ⮯ Maintaining ISO 13485 compliance is crucial for any company that wants to create medical devices that are reliable and efficient. To keep up with this worldwide standard, there are a few best practices that need to be followed. Organisations should set up explicit policies and processes for complying with ISO 13485. Regular reviews and any necessary updates should be made to these. All staff members should get training on both the standard’s requirements and the organization’s own rules and procedures. To make sure that all staff are following the right processes, regular audits should be carried out. Suppliers of the components, materials, and services utilised in the production of medical devices must also adhere to ISO 13485 standards. The company needs a system in place to keep track of the performance of its suppliers and ensure that they are adhering to the essential specifications. Any non-conformities found throughout the production process need to be fixed right away. To avoid repetition, the proper corrective and preventative measures must be done. It’s crucial to keep thorough records of all actions taken in connection with ISO 13485 compliance. This will make it easier to see any patterns or problem areas. ISO 13485 Certification process There are a few steps to getting ISO 13485 certified- The first stage is to create and publish a quality management system (QMS) that complies with ISO 13485. this QMS will need to be audited by a third-party, certified entity to guarantee compliance, the business can then apply for certification when the QMS has been accepted. The ISO certification procedure involves an initial examination by the certifying organisation, followed by several audits spread out over three years. Businesses need to keep up their QMS and continue to adhere to the criteria of ISO 13485 to keep their certification current. ISO 13485 Certification Cost ⮯ One of the most significant benefits of ISO 13485 certification for manufacturers of medical devices is the potential cost reductions. Depending on the size and complexity of the organisation, the cost of certification might vary, although it is often far less expensive than traditional quality management methods. Additionally, organisations having ISO 13485 certification may frequently meet their quality goals for a lesser cost than non-certified organisations. Conclusion ✅ Minor deviations from the norm are typically
Non-Conformity And Corrective Action

An organization is required by ISO 9001 to assess the necessity of taking steps to stop non-conformities from happening again. Customer complaints, bad or unfavorable results, trends from monitoring, reviews, assessments, or inspections, a failure to comply with legal or regulatory standards, or a failure to follow processes can all lead to nonconformities. As opposed to this, ISO 9001 is meant to prevent the inadvertent delivery or use of nonconforming outputs (outputs should be considered as products and/or services), and it requires that any nonconformity be controlled and repaired to prevent its unwanted use by or delivery to the customer. The only outputs (products and/or services) that an organization is required to deal with under the respective clause (8.7) are those that don’t adhere to the predetermined specifications. The identification of the nonconformity’s root cause and monitoring and evaluation of the success of the subsequent corrective action should serve as the first steps in the process of nonconformity and corrective action. Nonconforming tests or other work, customer complaints, internal or external audits, management evaluations, and staff observations can all lead to the need for corrective actions. Correction definition According to ISO 9000, correction (sometimes known as immediate correction) is the process of removing a nonconformity or flaw that has been identified. Along with taking remedial action, a correction can be made. Reworking the component, accepting the nonconformance through the concession procedure, replacing the product, or discarding the product are all possible corrections for product nonconformities. What is a remedial action? The fundamental cause(s) and contributing cause(s) of the undesirable condition, situation, nonconformity, or failure are addressed, and action is made to stop it from happening again. You must identify every reason (root cause and contributing causes) that has caused or may have caused an undesired state, situation, nonconformity, or failure as part of the corrective action process. When should remedial action be used ⮯ Depending on the level of risk, the appropriate level of management within the organization should decide whether or not to use the corrective action process. This advise offers a 6-step technique for taking corrective action and complying with each of these clauses’ obligations. There are numerous things that can start the corrective action process, for instance. -A potential threat to workers or the product’s safety;-Reliability or performance problems with the product;-High influence on operations for production and/or maintenance;-repetitive issues with a single activity or process, or issues that are similar in several activities and processes;-Detecting nonconformity is difficult; client request;-Significant problems with the management system; The location of complex issues that require outside assistance to resolve is not the issue itself. These certain outline the conditions that must be met for a nonconformity to occur as well as steps to take in order to avoid difficulties or nonconformities of a similar nature. Instead of seeking out blame or a department that is “more responsible than another,” the investigation of nonconformities should aim to identify and address the organizational flaws that led to them. A nonconformance report should be raised and appropriately entered into the nonconformity log whenever your internal audits find that your organization’s policy, objectives, standards, and other requirements as outlined in their management system are either not implemented at all or are implemented incorrectly. Prior to closure, the concerned Line Manager should be required to provide an accepted response. Both the corrective action and the root-cause must be addressed in order for the nonconformity to be resolved. Any non-conformities, the subsequent steps taken to stop them from happening again, and the success of the remedial action(s), should be well documented and kept. If any company requires a system and documents to help it manage the process of nonconformity and remedial action. Enjoy Reading – Non-Conformity Blog On ISO 9001 All You Need to Know about SOC Reports Significance of ISO 41001 for Industries Globally CMMI Certification: Optimising Processes To Achieve Goals
Major/Minor Non-Conformances : Explored In Detail

It is somewhere important for organizations to realize that their current business processes and associated procedures must bear high percentage of efficiency. But it is not possible when certain common non-conformities with standardized procedures occur at each phase where these typically occur. A checklist of such procedures will be helpful. A breaking down of each of the clauses and more in an effort to provide further clarity and guidance needs an utmost mention. What Is Non-Conformity? According to ISO 9001:2005, the definition of a nonconformity is “non-fulfilment of a requirement.” This basically indicates that a nonconformity occurs when you fail to meet the requirements set forth by the standard, your own documentation, or a third party. Here are a few nonconformities as examples: ⮯ If the standard calls for you to have records of corrective measures but you don’t, If your protocol calls for you to use a particular form for reporting the findings of your internal audit but you choose to use a different one If you didn’t provide your clients with specific reports even though you were required to per the agreement you entered into with them What is the importance of non-conformities? ⮯ Nonconformities are a “tool” that the auditor can use to determine the extent to which your management system complies with a standard. They are utilized in both internal and external (certification) audits. In other words, the more nonconformities you commit, and vice versa, the less compliant you are. An audit report must contain a nonconformity report, which is typically the longest section of the report. The auditor must include the following information when reporting the non-conformity: Give a brief, broad summary of the nonconformity and the problem. Provide audit-proof, such as by citing a specific document or record that is missing or being used incorrectly, an action that is not being completed or is being carried out inappropriately, etc. Refer to the precise requirement, such as a specific clause number from a standard, process, or contract. Rephrase what the standard, internal document, or contract specifies must be done to summarize the requirement. Major and Minor nonconformities’ distinctions The fundamental reason why major and minor nonconformities (as separate categories) are typically only used in certification audits and less frequently in internal audits is that if the auditor raises a major non-conformity, a company cannot obtain certification. What then qualifies as a serious nonconformity? This would be a non-conformity if it possessed any of the following traits: ⮯ The certification audit’s major versus small non-conformities. If a business entirely disregarded a mandated obligation, such as when it neglected to conduct a management review despite the standard’s need that it do so. If your process has entirely broken down, for instance, if you were supposed to perform backups every day but instead only did so sporadically over the month. If you have multiple minor nonconformities that are connected to the same procedure or component of your management system, such as multiple minor nonconformities related to your human resources department, such as some training records missing, some employees not receiving the proper training, some employment records missing, etc., this turns into a major nonconformity because it is obvious that something is seriously wrong with this division. If a certification mark is utilized improperly, such as when you tell your consumers that a product is ISO certified when, in fact, only the processes and management systems—not the actual products—are certified under the ISO management standards. If a minor nonconformity brought up during the prior audit is not fixed by the deadline, it immediately escalates to a major nonconformity. Small nonconformity is simple to define: It is any nonconformity that is not major. For instance, a small nonconformity might be that the backup was run every day of a certain month except for one. The key is to avoid placing yourself in a situation to experience a significant nonconformity. Make sure you truly implement the standard, not just for certification’s sake. An expert auditor will be able to tell if your system is merely theoretical, and you’ll likely receive a few significant non-conformities. Enjoy Reading – Non-Conformity Blog On ISO 9001 All You Need to Know about SOC Reports Significance of ISO 41001 for Industries Globally CMMI Certification: Optimising Processes To Achieve Goals
Non-Conformity Blog On ISO 9001:2015

A non-conformance in the context of ISO 9001 is when an organization does not adhere to the requirements of the standard. If you want to guarantee the quality of your organization’s processes, services, and products and maintain the satisfaction of your stakeholders, it is imperative that you understand what non-conformances to ISO 9001 are and how to deal with them. In-depth explanations of the various degrees of non-conformance and examples will be provided in this blog post for ISO 9001 non-conformance. It also looks at the effects of non-conformance and how to handle it. So, what does ISO 9001 non-conformance actually mean? The meaning of non-conformance is rather simple. It can be characterized as any situation in which your organization doesn’t follow ISO 9001 regulations. As you are aware, the International Organization for Standardization created the ISO 9001 standard. It defines the standards for a quality management system to make sure that your goods and services satisfy the requirements and expectations of customers, authorities, and the law. Therefore, non-conformances can appear in your procedures, goods, or even in the worker’s behaviour. Typically, non-conformances are found both during normal inspections and internal and external audits. They might range from minor faults that are simple to fix to significant flaws that have a negative impact on your conformity to ISO. What distinguishes minors from serious non-conformances? ⮯ An incident that does not adhere to ISO 9001 requirements but is a one-time occurrence and is not anticipated to have a significant impact on your QMS and business operations is referred to as a minor conformance. On the other hand, a large non-conformance might be either a series of lesser incidents or a single, serious incident that does not adhere to the standards of ISO 9001. Your QMS would be severely impacted, possibly causing complete corporate operations to be disrupted. No matter whatever category a non-conformance falls into, all non-conformances under ISO 9001 must be addressed through corrective activities that prevent the non-conformance from occurring again. Examples of ISO 9001 non-conformance Here are some instances of non-conformances you can encounter in your organization to put non-conformance into perspective: A lack of response to a decline in quality Improper process and procedure monitoring and measurement A staff member’s error Measurement requirements for the product don’t match the client’s expectations. Inadequate risk management and assessment An absence of corrective action documentation Not stating the ingredients used in your operations clearly Missing crucial records, including court records or training records What effects does non-conformance have? If non-conformances are not identified and handled, they may have a negative effect on your company. For instance, failing to address a decline in the quality of your products may lead to unhappy customers and a damaged reputation. The morale of your organization may suffer as a result of persistent personnel actions that violate ISO 9001 criteria. Additionally, manufacturing goods that don’t meet criteria may necessitate product recalls or restart of production, both of which reduce productivity. This will also not benefit your company in terms of retaining stakeholders’ satisfaction. What effects does non-conformance have? ⮯ Non-conformances are undesirable, but what matters most is how you handle them. After all, they are correctable. When a non-conformance is discovered, whether by you, an internal or external auditor, it is crucial that you take immediate action to rectify the situation. Filling out a Non-Conformance Report (NCR) is the initial step in handling a non-conformance. The document that follows: Tells the offender who is in charge of the violation Describes the non-conformance in detail and explain how it will be fixed so that it doesn’t happen again. You should implement the action plan you have created to address the non-conformance after completing an NCR. You should implement the action plan you have created to address the non-conformance after completing an NCR. A smart suggestion is to evaluate the success of your corrective measures in resolving the problem. You will be in a better position to make sure that your company complies with ISO 9001 regulations if you take these steps. Why is it crucial to comply with ISO 9001? By lowering the possibility of errors and saving you time, successful compliance to ISO 9001 can result in enhanced efficiency. Additionally, it helps increase the consistency of your systems and processes and aid in the ongoing development of your QMS. These advantages will ultimately result in happy employees and clients. Enjoy Reading – All You Need to Know about SOC Reports Significance of ISO 41001 for Industries Globally CMMI Certification: Optimising Processes To Achieve Goals
All You Need to Know about SOC Reports

What is SOC compliance? ⮯ The SOC Report, developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), is a verifiable auditing report produced by a Certified Public Accountant (CPA) detailing the systemic controls in place at a service provider, including Data security, Cybersecurity, Confidentiality, processing, reliability, Regulatory measures for financial reporting. SOC reports provide you with greater credibility, giving you a competitive edge that is both time and money well spent. There are three different SOC report types: SOC 1, SOC 2, and SOC 3. SOC 1 and SOC 2 are the two that are most often utilized. Insights on SOC 1, SOC 2 and SOC 3 SOC 1 The primary emphasis of SOC 1 is financial reporting. The objective is to establish internal controls and be able to demonstrate them for how you manage the financial information of your clients. Naturally, it is very important to your customers because they must provide this information to their auditors. SOC 1 compliance is all about demonstrating that you have the safeguards in place to guarantee that both the service’s actual operations and its design are reliable and predictable. SOC 2 SOC2 expressly covers the five elements of the Trust Services Criteria—security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. The SOC 2 report is a repeating report that shows that everything is right and compliant at a certain point in time. They may be disclosed to clients, executives, authorities, and other parties. A non-disclosure agreement could be required before sharing since they include sensitive information. SOC 3 SOC 3 reports emphasize the Trust Services Criteria controls as well. SOC 3 reports, however, can be disseminated extensively unlike SOC 2 reports. They provide a less thorough summary of the data and are referred to as “General Use” reports. It is usual for organizations to complete a SOC 2 and then have the auditors produce the SOC 3 summarizing the SOC 2 report since the same information as in a SOC 2 report has to be considered. They can serve as a useful marketing tool for illustrating how well your control environment works. Differences Between SOC1, SOC2 and SOC3 The primary distinction between SOC 1 and SOC 2 reports is that the former is more concerned with financial reporting, while the latter is with operations and compliance. SOC 3 is a variant of SOC 2 that was created for the clients of the firm, however, it is less prevalent. SOC 1 assesses an organization’s internal controls over financial reporting, whereas SOC 2 and SOC 3 analyze the organization’s control over one or more of the Trust Services Criteria. SOC 3, in contrast to SOC 2, is used to demonstrate publicly how effective an organization’s internal controls are. SOC 1 reports are intended for auditor-to-auditor communication. SOC2 can be shared with customers, management, regulators, and third parties and SOC3 reports are considered “General Use” reports but offer a less detailed summary of the information. Impact of SOC on Organisation ⮯ An organization’s overall security is improved through a security operations center’s overarching approach, threat management, which entails gathering information and checking it for unusual activities. Firewalls, threat intelligence, intrusion prevention and detection systems (IPSes/IDSes), probes, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems are some of the sources of the raw data that SOC teams monitor. If any of the data is unusual or exhibits indicators of compromise (IOCs), alerts are generated to notify team members as soon as possible. What are the Benefits of SOC Audits? ⮯ SOC 1, SOC 2, and SOC 3 audits are intended to accomplish various goals. Financial reporting is the main emphasis of SOC 1 compliance, but SOC 2 and SOC 3 have a broader perspective and are more appropriate for organizations that provide technical services. The primary distinction between SOC 2 and SOC 3 is whom they are designed for. Think about the target market and your company’s business strategy when deciding which SOC to pursue. SOC 2 is the best option if you exclusively work with non-financial data and want to show your customers your competence. A SOC 1 audit might be quite helpful if you need to comply with Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) when your business becomes publicly traded. The only benefit of a Type 1 audit over a Type 2 audit is that it is completed more quickly. Since most clients are aware of the limitations of a Type 1 audit, they will be searching for Type 2. Conclusion ✅ The most popular SOC reports all have distinct purposes, but it can be challenging for a service provider to choose which one is right for them. The choice between SOC 1 and SOC 2 relies on how much your controls affect a client’s internal control over financial reporting. Remember that a SOC 2 audit report is a restricted-use document that contains information on the systems and procedures in place for protecting information if you are SOC 2-compliant but are unsure if a SOC 3 audit report is best for you. Enjoy Reading – Significance of ISO 41001 for Industries Globally CMMI Certification: Optimising Processes To Achieve Goals What is the Implementation Checklist of ISO 22301 Certification
Significance of ISO 41001 for Industries Globally

ISO 41001:2018 is the internationally recognised standard used worldwide related to the Facility Management system(FMS). The standard offers a framework for managing facilities effectively and economically, and it addresses every facet of facility management, from planning and design to operation and maintenance. Facility Management Systems may assist facility managers in enhancing operational effectiveness, resource allocation optimisation, safety and security enhancement, and regulatory compliance connected to building operations. ISO 41001:2018 is relevant to all organisations regardless of sector, size or location. The best practices from throughout the world are examined and reported to develop the ISO 41001:2018 certification. This standard gives businesses a wide range of options for action that will enable them to deliver strategic planning at new standards, create tactics, and enhance new plant management. ISO 41001:2018 helps industries ensure that their facility management processes are efficient and cost-effective. Additionally, it provides guidance on how to improve existing processes and ensure compliance with legal requirements. By implementing ISO 41001:2018, industries can demonstrate their commitment to providing quality services while also improving safety standards and reducing operational costs. This makes it a valuable tool for any industry looking to improve its facility management operations on a global scale. Adopting this standard can bring numerous benefits to industries, including improved efficiency in managing resources, better communication between departments, and increased customer satisfaction. However, there are several challenges related to adopting and implementing ISO 41001 in different organizations. These include the cost of implementation, lack of understanding about the standard, difficulty in measuring compliance, lack of resources to implement it effectively, and resistance from employees. Overall, having effective Facility Management Systems in place is essential for any industry looking to remain competitive in today’s global market. Some of the core benefits of ISO 41001 for industries globally Industries may reduce facility-related risks by identifying and addressing them with ISO 41001, which can help avoid mishaps, injuries, and other occurrences. A facility management system standard eliminates trade restrictions and opens up the global market. It demonstrates a company’s capacity to integrate global best practices into its management system. The standard provides guidance on developing policies and procedures that all stakeholders can use in the organisation. It provides higher efficacy and efficiency, which results in greater cost savings for the organisation. It guarantees continued competitiveness on a national and worldwide scale. It helps an organisation to adopt tools and approaches to manage the constantly evolving trends in infrastructure development. Conclusion ✅ The importance of ISO 41001 lies in its ability to help organizations improve their facility management processes and reduce costs associated with managing their facilities. This leads to establishing a culture of increased productivity and increased profitability for businesses. It also helps in reducing environmental impact by minimizing energy consumption and waste production. It makes sure that organizations ensure compliance with local regulations and industry standards. Additionally, it can help organizations to improve their growth by providing better services and improved safety measures. Enjoy Reading – 10 Benefits of Getting ISO 41001 Certification for Facility Management System ISO 45001 Certification Process in Singapore Why is ISO 27001 Important These Days
CMMI Certification: Optimising Processes To Achieve Goals

When it comes to choosing a CMMI certification, there are a lot of things to consider. But don’t worry, we’re here to help! In this blog, we’ll discuss the different types of CMMI certifications, the benefits of each, and what you need to know in order to choose the right one for you. By the end, you’ll be armed with all the knowledge you need to make an informed decision about which CMMI certification is right for you. So what are you waiting for? Let’s get started! What Is the CMMI Model? CMMI, or the Capability Maturity Model Integration, is a model that organizations can use to improve their software development processes. The CMMI model was created in 1989 by the Software Engineering Institute (SEI), a branch of Carnegie Mellon University. The CMMI model is divided into five main maturity levels : Initial, Managed, Defined, Quantitatively Managed, and Optimising. Each maturity level has its own set of goals and objectives that organizations can strive to achieve in order to improve their software development processes. Overview of CMMI Certifications So, you’re interested in Capability Maturity Model Integration CMMI certifications ? Excellent choice! This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the different types of CMMI certifications available, so you can choose the one that’s right for you. We’ll start by discussing the different levels of certification available, so you can get a sense of what each one entails. Then we’ll go over the different types of exams available, and help you decide which is the best fit for your skills and knowledge. We’ll also provide tips on how to prepare for your exam, and give you a sneak peek at what to expect on the day of the test. By the end of this guide, you’ll be ready to take the plunge and get certified! What is CMMI Level? ⮯ CMMI focuses on process improvement in an organization with proven ways of doing business. This is not a random way of doing business but involves methods that evaluate and measure the maturity of the software development process on a scale of 1 to 5. Though CMMI was originally developed to improve the Software Development processes of an organization eventually it was also introduced into – System Engineering Software Acquisition Supplier Sourcing People CMM What is CMMI Level 1? At maturity level 1 (CMMI Level 1) processes are at a very rudimentary stage that is quite chaotic. The organization is at a pre-mature stage in which individual success defines the overall performance of the organization. The company is still not working with the proven processes that come with institutional authenticity. What is CMMI Level 1? At maturity level 1 (CMMI Level 1) processes are at a very rudimentary stage that is quite chaotic. The organization is at a pre-mature stage in which individual success defines the overall performance of the organization. The company is still not working with the proven processes that come with institutional authenticity. What is CMMI Level 2? At maturity level 1 (CMMI Level 1) processes are at a very rudimentary stage that is quite chaotic. The organization is at a pre-mature stage in which individual success defines the overall performance of the organization. The company is still not working with the proven processes that come with institutional authenticity. What is CMMI Level 2? At maturity level 1 (CMMI Level 1) processes are at a very rudimentary stage that is quite chaotic. The organization is at a pre-mature stage in which individual success defines the overall performance of the organization. The company is still not working with the proven processes that come with institutional authenticity. What is CMMI Level 3? If you’re considering CMMI certification Level 3 for your business, it’s important to understand the process involved. The CMMI certification program consists of five main stages: appraisal planning, initiation and composition of the appraisal team, appraisal execution, appraisal completion and report generation, and report review & results presentation. At each stage, the team evaluates specific aspects of the organization’s performance such as strategic planning, risk management, customer satisfaction, and organizational learning. During the appraisal execution stage, a detailed assessment is done in order to identify and document current capabilities as well as areas of improvement. Finally, at the report review & results presentation stage, all findings are discussed and potential solutions are proposed to reach Level 3 status. While this process can be quite lengthy and time-consuming, following through with it all is key to achieving Level 3. So be sure to read up on each step thoroughly before proceeding with CMMI certification! What is CMMI Level 4? At maturity level 4 the overall process performance is the result of sub-processes that are selected to fructify the needs of customers, end users, organizations and process implementers. The involved sub-processes are controlled using statistical and other quantitative techniques. The inclusive criteria in managing processes have been set through the quantitative objectives. The organizational measurement repository is aligned with the quality and process performance measures to support fact-based decision-making in the future. What is CMMI Level 5? At Capability Maturity Model Integration CMMI Maturity Level 5 the most significant area of process improvement that an organization works on is the quantitative understanding of business objectives. Here the organization is entirely dedicated to implementing innovative processes and technological improvements that get continually revised to reflect changing business objectives. The ensuing effects of the deployed process improvements are measured using quantitative and other statistical techniques which are compared to the quality and process performance objectives. What is SCAMPI? ⮯ Organizations need a SCAMPI lead appraiser to help the team “achieve a level.” that is the result of the Standard CMMI Appraisal Method for Process Improvement (SCAMPI). It is the appraisal method that exists at different types of appraisals, called “Classes”. These can be distinguished as SCAMPI A, SCAMPI B, or SCAMPI C.. Benefits and Challenges of Obtaining a CMMI Certification ⮯ If you are thinking of getting a CMMI certification it can bring a lot of benefits
A Guide to Facility Management System (FMS)

“If you want to have a profitable business, you need to have an efficient business.” A business earning good profit is considered a successful business organization. But earning profits shows an organization’s standard, not its priority. A business organization’s main aim is to provide customers facility and make their life comfortable and easy. The effectiveness and efficiency of an organization are measured by its ability to provide disruptive services to its customers. No organization can predict the unpredictable, but we always have a choice to prepare ourselves beforehand. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed ISO 41001 Certification to ensure that a business remains operating and provides a safe and productive environment to its employees. Facility Management System ISO 41001 Certification outlines the requirements for Facility Management System (FMS) standard. It provides a framework for organizations to integrate multiple business processes and activities into a single structure to increase production and productivity. It encompasses a broad range of activities and affects organizations, communities, societies, and economies. ISO 41001 Certification provides tools and techniques for an organization to make the entire supply chain more efficient. It follows the Annex SL structure and helps organizations to cultivate, implement, and maintain an effective facility management system globally. Which Organizations Can go for ISO 41001 Certification? ⮯ ISO 41001 certification is a generic standard, and any organization can apply for ISO 41001 certificate, regardless of its size, nature, and location. Implementing ISO 41001 standards within the organization improves an organization’s facility management performance. A list of organizations that can apply for ISO 41001 certification :- How ISO 41001 Certification is Beneficial for Organizations? ISO 41001 certification offers the following benefits to an organization :- ISO 41001 certification shows that an organization fulfils all the legal and regulatory requirements to establish an effective facility management system. It exhibits an organization’s compliance with all national and international laws, regulations, and standards. It helps organizations to avoid regulatory fines and penalties. ISO 41001-certified organizations achieve a competitive edge in the market. A facility management system standard demonstrates an organization’s ability to implement international best practices within the management system. It enhances an organization’s market image and boosts the confidence of customers and other stakeholders in your brand. ISO 41001 certificate helps organizations win new businesses, clients, and customers. Organizations that are ISO 41001- certified use ISO 41001 certificate as a marketing tool to improve their profitability. It increases an organization’s turnover and expands its customer base. ISO 41001 standards follow a risk-based approach to identify potential risks and opportunities that might impact business operations and activities. It implements appropriate tools and controls to address them accordingly. It is a cost-effective standard that helps organizations save money that they spend on paying premiums and compensation. ISO 41001 standards aim to provide a better experience to employees. It focuses on establishing more supportive, sustainable, and productive workplaces. The process to get an ISO 41001 Certification ⮯ Conducting gap analysis – An organization must conduct a gap analysis to check and measure the effectiveness and efficiency of the facility management system. It helps organizations identify the gaps between the existing facility management system and ISO 41001 certification standards. Creating awareness and providing training – It requires an organization to provide necessary training and create awareness among employees and management. An organization must educate its employees and management on the importance of ISO 14001 certification. Maintaining documentation and records – It requires an organization to provide guidance regarding documentation and implementation of ISO 41001 Certification. Conducting risk assessment – An organization shall conduct a risk assessment to identify potential risks that might cause unintended outcomes. It provides appropriate tools and controls for organizations to address them accordingly. Performing internal audit – An internal audit prepares an organization for the external audit. External Audit – Conduction of an external audit by the certification body. Feedback – The certification body shares the feedback and closure of observation with the organization. Certification – Issuance of an ISO 41001 Certification. Surveillance Audit – An organization must Conduct periodic surveillance audits to measure ISO 41001 certification compliance. Conclusion ✅ ISO 41001 is a Facility Management System (FMS) standard. It integrates various business activities and processes to improve production and productivity. ISO 41001 Certifications covers a broad range of activities improves the reputation of an organization and helps in winning new business, clients, and customers. It is a generic standard and any organization can organization apply for ISO 41001 certification as it enhance the profitability and marketability of an organization. Enjoy Reading – 10 Benefits of Getting ISO 41001 Certification for Facility Management System ISO 45001 Certification Process in Singapore Why is ISO 27001 Important These Days
